What is a Raspberry Pi?
The Raspberry Pi device looks like a motherboard, with the mounted chips and ports exposed (something you’d expect to see only if you opened up your computer and looked at its internal boards), but it has all the components you need to connect input, output, and storage devices and start computing.
Raspberry Pi Overview
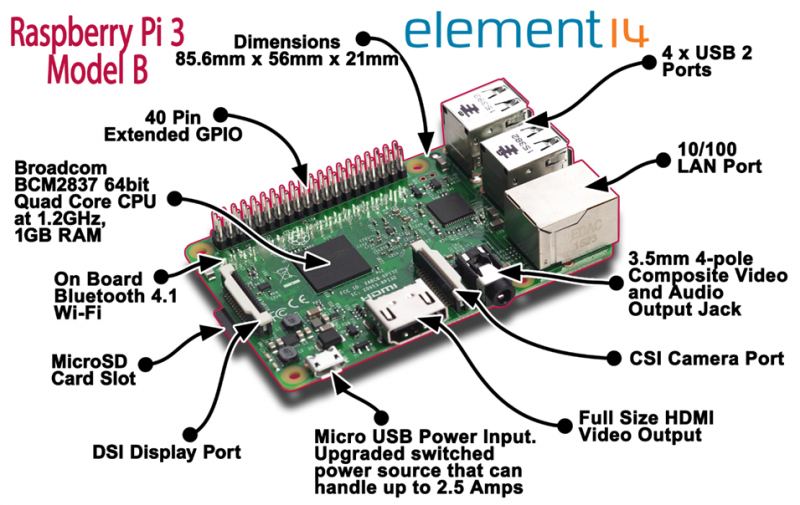
Component Explanations
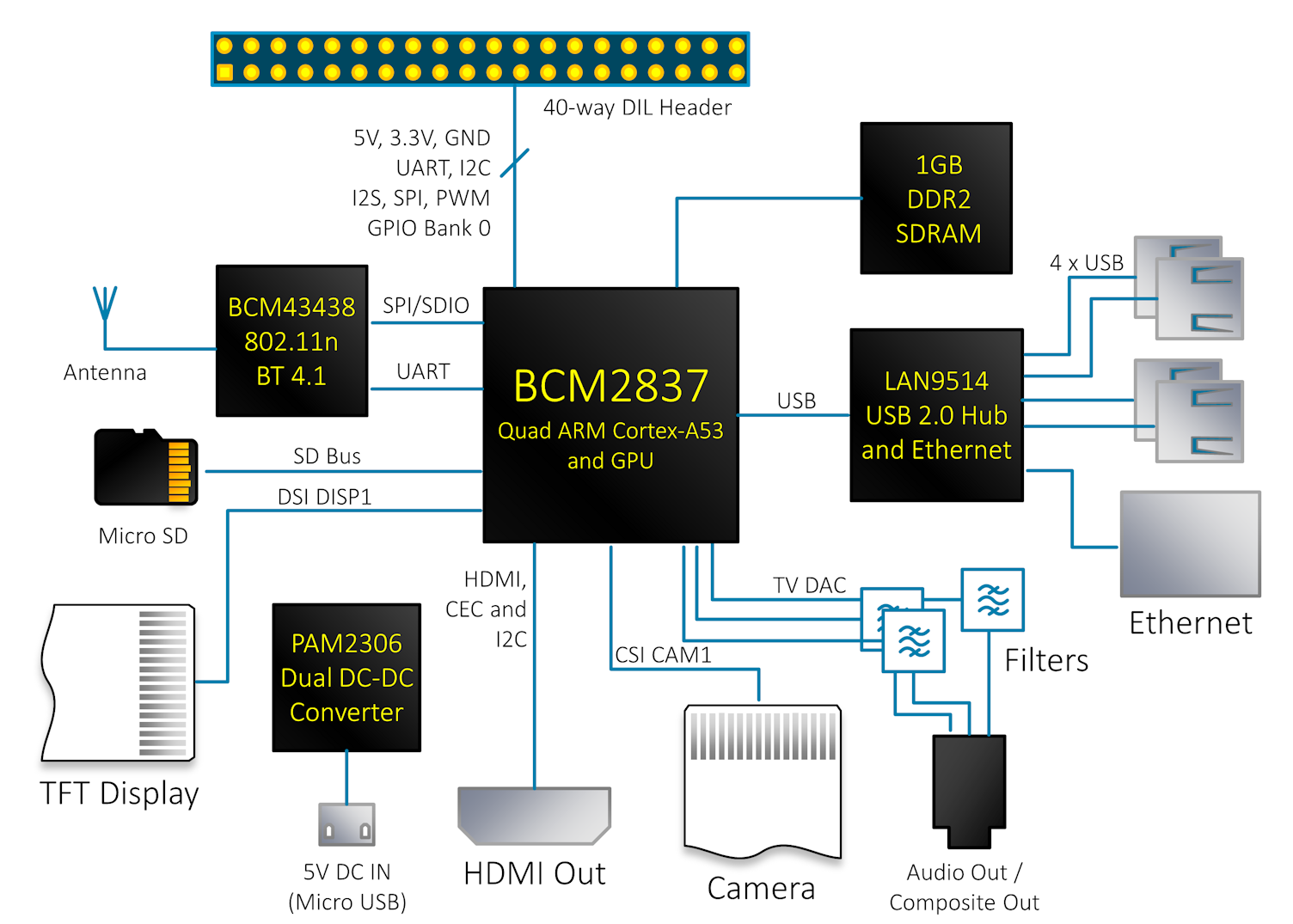
- ARM CPU/GPU — This is a Broadcom BCM2835 System on a Chip (SoC) that’s made up of an ARM central processing unit (CPU) and a Videocore 4 graphics processing unit (GPU). The CPU handles all the computations that make a computer work (taking input, doing calculations and producing output), and the GPU handles graphics output.
- GPIO — These are exposed general-purpose input/output connection points that will allow the real hardware hobbyists the opportunity to tinker.
- Audio out — This is a standard 3.55-millimeter jack for connection of audio output devices such as headphones or speakers. There is no audio in.
- LEDs — Light-emitting diodes, for all of your indicator light needs.
- USB — This is a common connection port for peripheral devices of all types (including your mouse and keyboard). Model A has one, and Model B has two. You can use a USB hub to expand the number of ports or plug your mouse into your keyboard if it has its own USB port.
- HDMI — This connector allows you to hook up a high-definition television or other compatible device using an HDMI cable.
Power — This is a 5v Micro USB power connector into which you can plug your compatible power supply. - SD cardslot — This is a full-sized SD card slot. An SD card with an operating system (OS) installed is required for booting the device. They are available for purchase from the manufacturers, but you can also download an OS and save it to the card yourself if you have a Linux machine and the wherewithal.
- Ethernet — This connector allows for wired network access and is only available on the Model B or later.
Block Diagram